The Role of an Audiologist in Hearing Loss Treatment
When experiencing and managing hearing loss, you’ll often hear the
Knowledge is power on the road to better hearing, which is why we provide helpful resources and support beyond your office visit. On the blog, you’ll find articles covering topics such as hearing aid maintenance, hearing loss management and more.
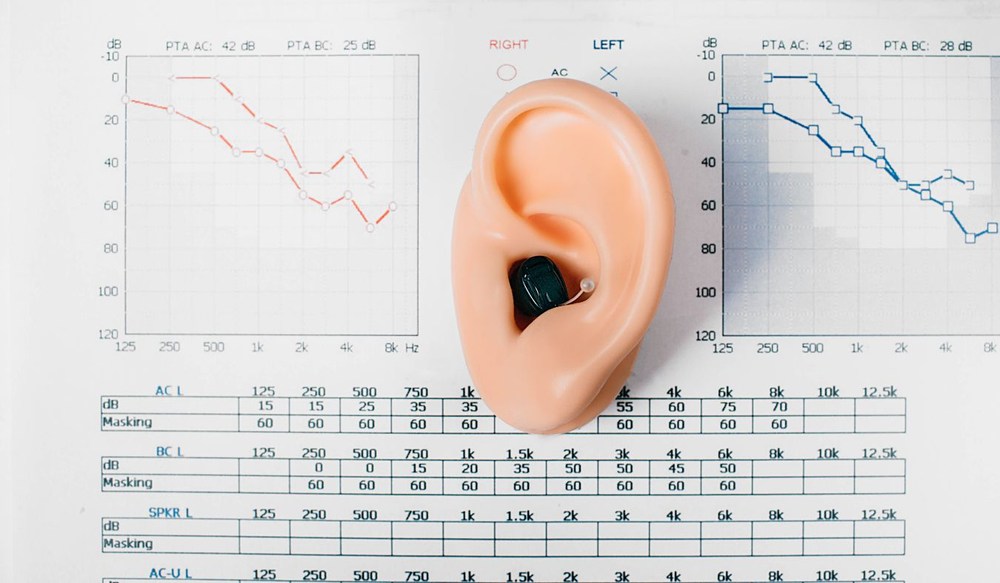
When spring arrives, many of us deal with the typical symptoms of seasonal allergies – runny noses, watery eyes and sneezing. What you might not realize is that these allergies
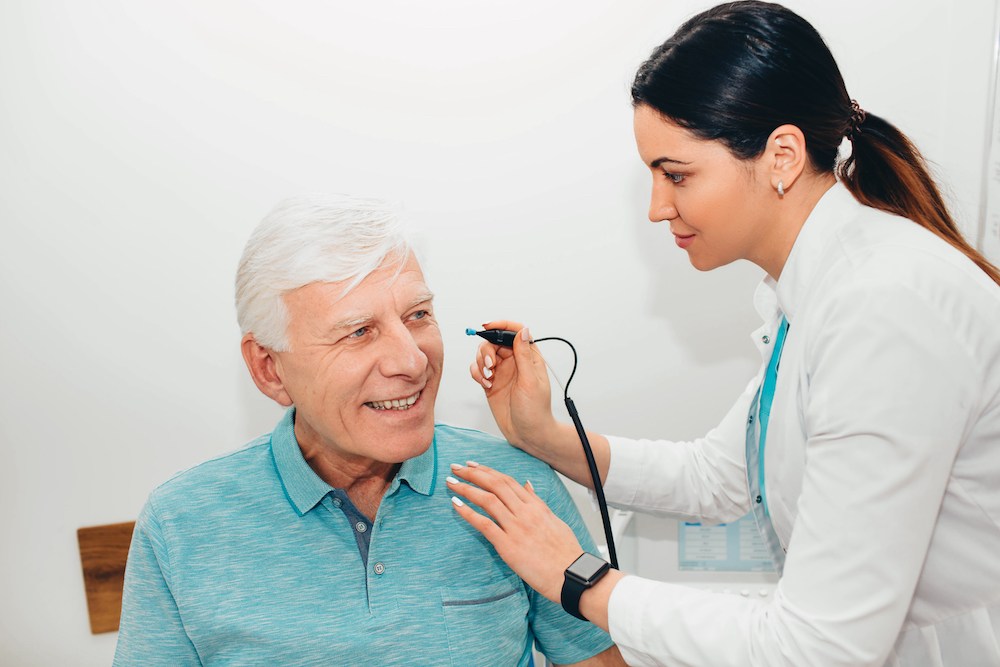
When spring arrives, many of us deal with the typical symptoms of seasonal allergies – runny noses, watery eyes and sneezing. What you might not realize is that these allergies
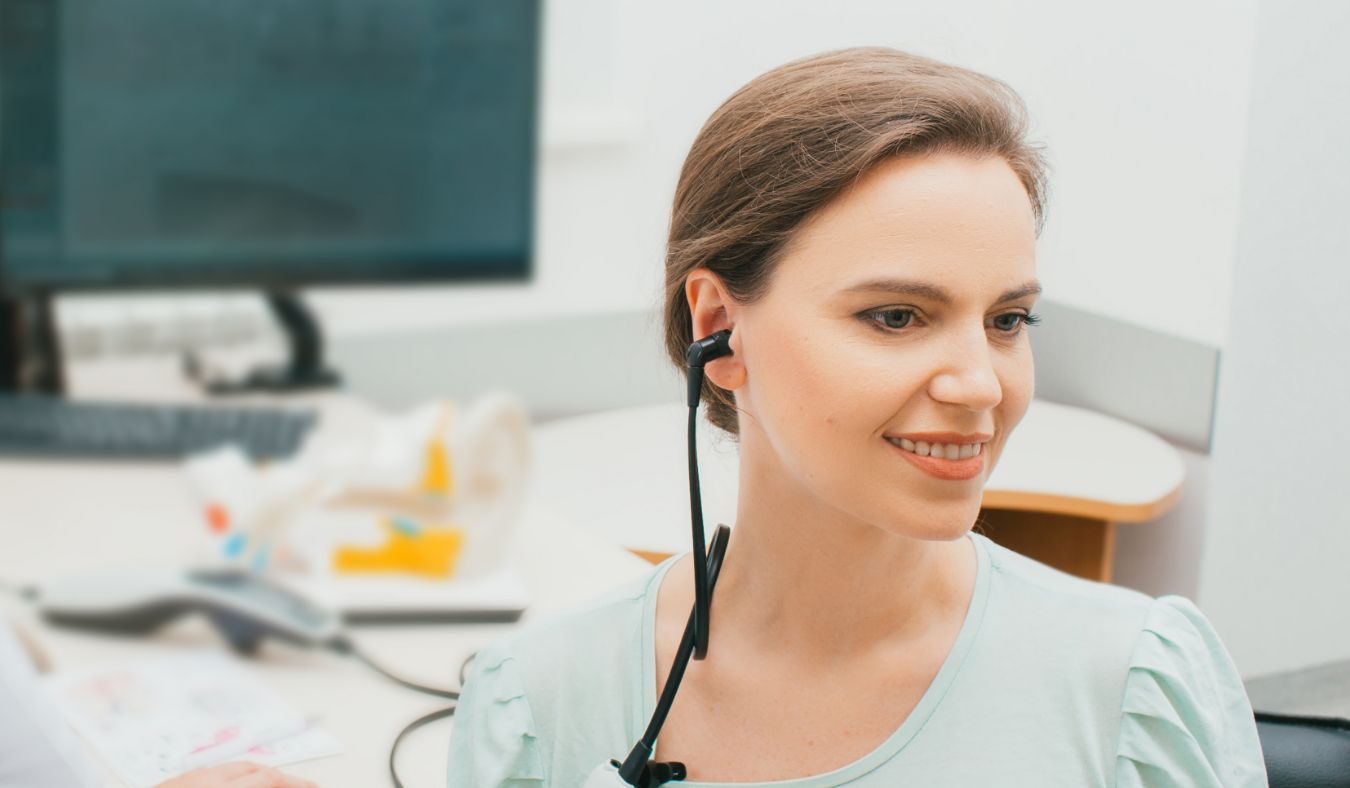

When spring arrives, many of us deal with the typical symptoms of seasonal allergies – runny noses, watery eyes and sneezing. What you might not realize is that these allergies
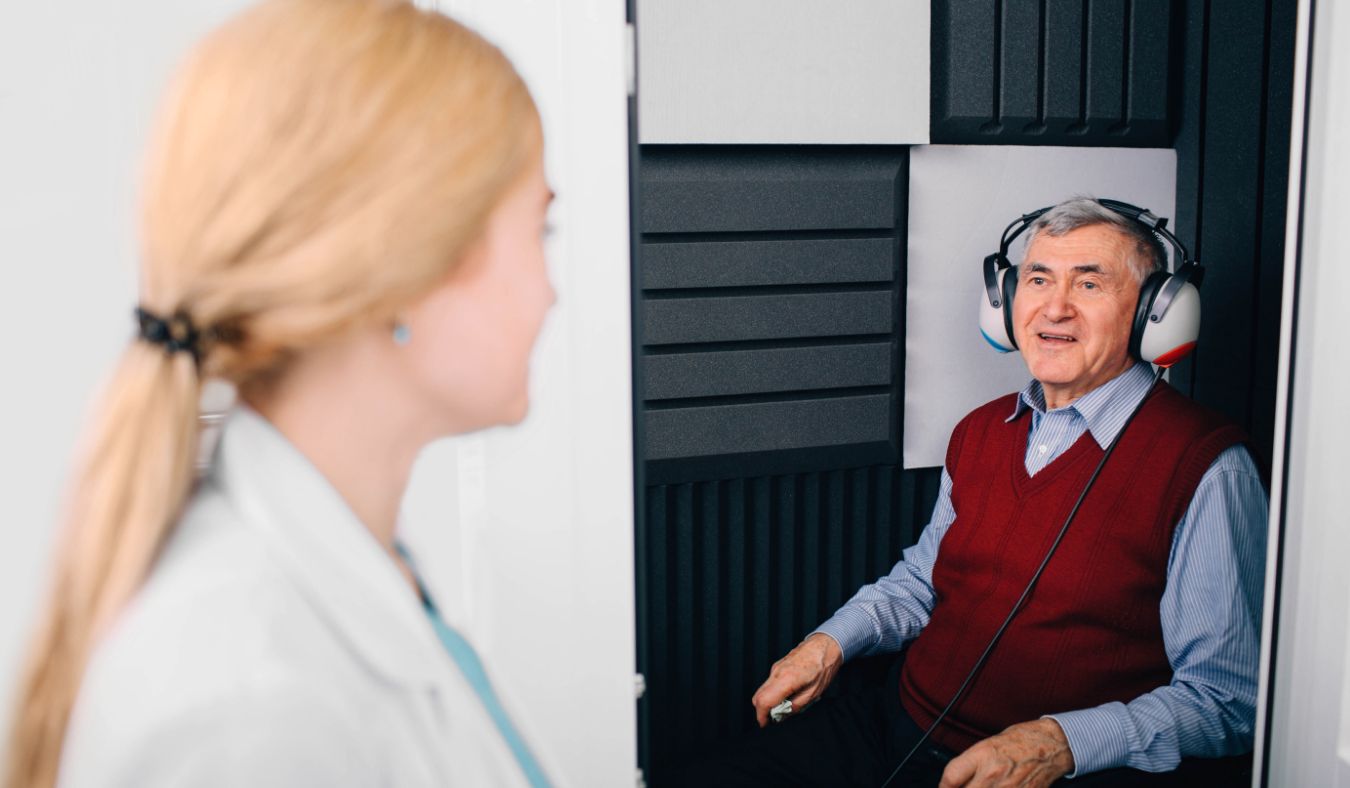

When experiencing and managing hearing loss, you’ll often hear the

Imagine this: It’s a peaceful Sunday morning. You’re enjoying

In today’s increasingly remote and hybrid work environments, effective

There are many different types of hearing aids to choose from these days.

If you’ve been following our blog over the past year, you might recall

Hearing loss can be a challenging and often overwhelming experience. With